"Optimus": A Threat to Mankind?
June 01, 2023
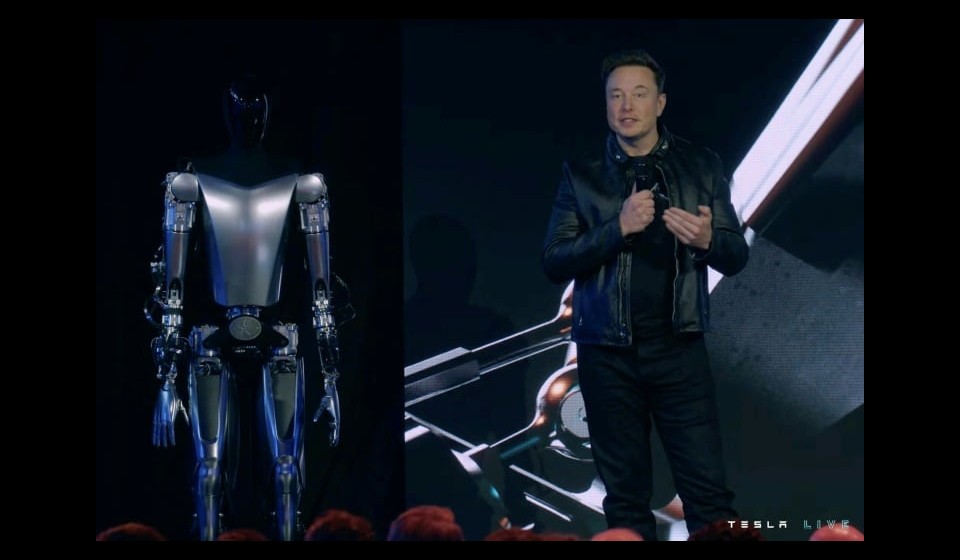
Image ©https://www.enca.com/life/no-terminator-musk-teases-useful-humanoid-robot
Article by Mariam Dzidzikashvili
Source GZAAT STEM Journal
Asteroids are rocky remnants left from the formation of our solar system 4.6 billion years ago.1 There are over 1 million asteroids located in our galaxy. Approximately once every 2000 years, an asteroid, the size of a football field, strikes the surface of the earth and causes damage.2 Luckily, an asteroid that could impact Earth's civilization (like the one that annihilated the dinosaurs) only comes around once every few million years. Earth's atmosphere provides a natural defense against asteroids, so most of them just burn up when they enter it, causing only a little bit of damage at most.3
For a long time, Earth's atmosphere was the only thing protecting it from a possible threat, “Asteroids.” Luckily that is not the case anymore. Earth's planetary defense conducted the first full-scale demonstration of deflection technology, which achieved great success.4
DART, short for double asteroid redirection test, is planetary defense’s first test mission. Its goal was to alter asteroid Dimorphosys’s orbit around its parent asteroid Didymos by smashing a spacecraft into it. It was a trial run of a technology that one day could save the Earth from a possible asteroid collision. After its success in changing Dimorphosys trajectory, it became one of the best investments that Nasa has ever made.5
As previously mentioned, there are over 1 million asteroids in our galaxy. So, why was Dimorphous chosen for this mission? Well, the answer is quite simple. Dimorphous and Didymos are easy to observe from the Earth. Satellites of the Earth are capable of noticing the occurrence of any changes and telling the exact time it takes Dimorphous to orbit Didymos. The location of Dimorphous is 11 million kilometers from Earth. This location was safe because the asteroids posed no threat and this distance made it possible to reach the asteroids quite fast. Reaching asteroids only took 10 months, which is quick for a space mission.6
The spacecraft managed to successfully shift an asteroid's orbit, proving that it is possible to alter an object's trajectory in space. In order to confirm their success, scientists measured the brightness of the asteroid with ground-based telescopes. This allowed researchers to determine how rapidly Dimorphous was circling Didymos. Before the impact, it took Dimorphous 11 hours 55 minutes to orbit Didymos, while after the impact it took only 11 hours 23 minutes. Thus, the time required to orbit an asteroid changed by 32 minutes.
This test mission was to prove that it was possible to defend ourselves from the asteroids. Most people might think that the real problems are the large asteroids that can annihilate the human race, but that is not the case since they only threaten the Earth once every few million years. Of course, those asteroids are very dangerous. However, Nasa is more concerned about small asteroids like Dimorphous.7 Small asteroids pose a threat much more often, approximately every 200 years. Though they might not be as catastrophic as the big ones, they are still very dangerous and can cause a lot of damage to Earth and its population. Since it is more likely for a smaller asteroid to hit Earth first, currently, they pose a big threat. There are several examples of near - Earth small asteroids causing damage to the Earth. The biggest event occurred in February 2013, in the city of Chelyabinsk, when an asteroid with a diameter of 20 meters entered the Earth's atmosphere. Less than 0.05% of the asteroid landed on the Earth, however it exploded 30 kilometers up in the atmosphere and caused a flash of light brighter than the sun. The asteroid damaged many buildings, caused severe sunburns and injured 1500 people. A similar situation occurred 105 years earlier (in 1908) called the Tunguska event. It happened almost 1500 kilometers from Chelyabinsk and flattened 200 square kilometers of the forest, destroying around 80 million trees. It was caused by a 36-meter-wide asteroid that fragmented around 5 to 10 kilometers up in the atmosphere. Around 2.8million tons of TNT was released when the asteroid shattered(185 times more energy than the atomic bomb fired on Hiroshima). This kind of asteroid would have caused a lot more trouble if the situation had occurred over a major city.8
Thanks to Nasa, humanity has gained yet another defense from the constant threat of nature. In this case: asteroids. DART is a huge success and will most definitely go down in history. However, NASA describes it only as a first step. DART was simply a test-run and the first ever demonstration, but its success proved that humans can alter the trajectory of further threats posed by asteroids in the future. With the improvement of space technologies, the human race will be able to outlive dinosaurs and live in peace, not fearing the threat posed by asteroids any further.
Works Cited:
Kelly, Jack. “Sophia—the Humanoid Robot—Will Be Rolled out This Year Potentially Replacing Workers.” Forbes, 6 Jan. 2021
www.forbes.com/sites/jackkelly/2021/01/26/sophia-the-humanoid-robot-will-be-rolled-o ut-this-year-potentially-replacing-workers/?sh=6b5771a96df2. Accessed 16 Jan. 2023. Magazine, Smithsonian, and Margaret Osborne. “Elon Musk’s New Humanoid Robot Might One Day Buy Your Groceries.” Smithsonian Magazine, 4 Oct. 2022,
www.smithsonianmag.com/smart-news/elon-musks-new-humanoid-robot-might-one-daybuy-your-groceries-180980884/. Accessed 16 Jan. 2023.
McCallum, Shiona. “Tesla Boss Elon Musk Presents Humanoid Robot Optimus.” BBC News, 1 Oct. 2022, www.bbc.com/news/technology-63100636. Accessed 16 Jan. 2023